Compliance deadlines come fast in property management. Miss a tax filing, skip a safety inspection, or overlook a tenant notice requirement, and you’re looking at penalties ranging from hundreds to tens of thousands of dollars. The difference between compliant property managers and those facing legal trouble often comes down to one thing: a systematic compliance calendar.
A Property Management Compliance Calendar organizes every regulatory deadline, inspection, certification, and legal obligation you must meet throughout the year. It’s not just a planning tool; it’s your protection against fines, lawsuits, and license revocations.
This 2026 compliance guide breaks down exactly what you need to do each month to stay compliant with federal, state, and local regulations. Whether you manage residential apartments, commercial properties, or affordable housing, this checklist keeps you on track.
What Makes a Property Management Compliance Calendar Essential?
Property managers juggle dozens of regulatory requirements from multiple government agencies. The IRS wants 1099 forms by January 31. HUD requires fair housing compliance year-round. OSHA mandates workplace safety documentation. Your state sets security deposit return deadlines. Local building departments schedule annual inspections.
Without a centralized system tracking these obligations, something will slip through. And compliance failures carry serious consequences:
- Financial penalties start at $60 per missed 1099 form and climb to $75,000 for Fair Housing Act violations, $150,000 for repeat ADA violations, and $27,500 per day for environmental violations.
- Legal consequences include civil lawsuits with compensatory and punitive damages, class actions from tenant groups, criminal charges for intentional discrimination, and loss of property management licenses.
- Operational damage means reputation harm, contract terminations from property owners, increased insurance costs, staff turnover, and reduced property values.
A compliance calendar prevents these outcomes by converting complex regulations into manageable monthly tasks. Effective property management requires systematic organization compliance is no exception.
How Do You Build an Effective Compliance Calendar for 2026?
Start by inventorying every compliance obligation your properties face. Federal requirements apply nationwide, but state and local rules vary significantly.
- Federal compliance includes Fair Housing Act protections (seven protected classes), ADA accessibility requirements, IRS tax reporting (1099 forms, W-9 collection), OSHA workplace safety standards, and EPA environmental regulations for lead paint and asbestos.
- State requirements cover landlord-tenant laws (eviction procedures, rent increase limits), security deposit regulations (amounts, return timelines, interest payments), contractor licensing rules, and state tax registrations.
- Local obligations involve building safety inspections, certificate of occupancy renewals, business license renewals, local health and fire inspections, and municipal ordinances for trash, pest control, and noise.
- Property-type specific rules apply differently. Residential properties need lead disclosures for pre-1978 buildings. Commercial properties require ADA compliance in public areas. Affordable housing demands strict income recertification schedules and HUD inspections.
Once you identify your specific obligations, organize them by deadline. Use property management software with automated reminders, or create a shared calendar with tasks assigned 30, 14, and 7 days before each deadline. Document management helps track compliance certificates, insurance policies, and inspection reports in one secure location.
What Are the Critical January Compliance Deadlines?
January brings the year’s most critical tax deadline: January 31 for all 1099 forms.
- Form 1099-NEC reports payments to contractors, plumbers, electricians, landscapers, property managers (if you manage for others), accountants, and attorneys. If you paid anyone $600 or more for services during 2025, they need a 1099-NEC per IRS requirements.
- Form 1099-MISC reports rent payments to property owners (Box 1) and attorney fees (Box 10). Both recipient copies and IRS filing are due January 31, with no extensions available.
Critical steps:
- Verify W-9 forms on file for all vendors and property owners
- Run year-end payment reports by vendor
- Generate 1099 forms (electronic filing required if you issue 10 or more)
- Mail recipient copies by January 31
- File with the IRS by January 31
Missing this deadline triggers penalties starting at $60 per form and climbing to $310+ for forms filed after August 1. For property managers issuing dozens of 1099s, penalties add up fast.
Other January priorities:
- Review and renew property insurance policies
- Schedule annual property inspections for the year
- Update Fair Housing policies and procedures
- Plan quarterly staff training schedule
- Complete annual budgets and forecasts
Financial reporting makes tax season significantly easier when your vendor payments and owner distributions are tracked accurately throughout the year.
What Safety and Regulatory Tasks Should You Complete in February–April?
February: Safety Compliance Focus
February 1 marks a critical OSHA deadline: posting Form 300A Summary. This summary of workplace injuries and illnesses from the previous year must remain posted in a conspicuous location through April 30.
Property managers with employees (maintenance staff, leasing agents, office workers) must maintain OSHA Form 300 throughout the year, logging all work-related injuries and illnesses. The annual summary shows total cases and must be certified by a company executive.
February tasks:
- Post OSHA 300A summary by February 1
- Conduct Q1 Fair Housing training for all staff
- Inspect properties for winter damage (roof leaks, frozen pipes, ice dams)
- Review heating system performance
- Deliver year-end financial statements to property owners
- Verify snow removal contract compliance
March: Spring Preparation
March 31 is the deadline for electronic 1099 filing if you filed 10 or more forms. If you filed paper copies in January, this doesn’t apply, but electronic filing is now mandatory at the 10-form threshold.
March tasks:
- Complete electronic 1099 filing if applicable
- Schedule spring property inspections
- Arrange HVAC maintenance for cooling season
- Review lease expirations for next 90 days
- Audit all marketing materials for fair housing compliance
- Update tenant screening procedures
April: Tax Returns and Safety Wrap-Up
April 15 brings business tax return deadlines and quarterly estimated tax payments. April 30 is when you remove the OSHA 300A summary from display.
April tasks:
- File business tax returns (partnerships, S-corps, C-corps have varying deadlines)
- Make Q1 estimated tax payments
- Remove OSHA 300A summary after April 30
- Begin pool opening preparations for summer
- Schedule fire safety drills for buildings
Which Summer and Fall Compliance Activities Matter Most?
May–June: Peak Leasing Season
May 1 brings energy benchmarking deadlines in cities like New York (Local Law 84 requires annual energy reporting for buildings over 25,000 square feet). Verify your city’s requirements.
May tasks:
- File energy benchmarking reports (select cities)
- Ramp up leasing operations for summer turnover
- Conduct fire safety drills in multi-family buildings
- Service air conditioning systems before summer heat
- Review mid-year budget performance
- Update capital improvement plans
June tasks:
- Q2 estimated tax payments (June 15)
- Review vendor contracts and request renewal bids
- Inspect roofs, gutters, and drainage after spring storms
- Plan for summer maintenance projects
July–September: Mid-Year Review and Planning
Use the summer months for compliance audits before year-end rushes.
July–August tasks:
- Conduct mid-year compliance audit (Fair Housing procedures, ADA accommodation logs, safety equipment, vendor insurance certificates)
- Refresh staff training on key compliance areas
- Inspect and service HVAC systems
- Review and update emergency response procedures
- Verify all business licenses and registrations remain current
September tasks:
- Make Q3 estimated tax payments (September 15)
- Begin year-end tax planning (vendor payment summaries, equipment purchases)
- Prepare HVAC systems for heating season
- Review accommodation request documentation
- Schedule fall property inspections
October–December: Year-End Compliance
The final quarter requires preparation for next year’s reporting.
October–November tasks:
- Run vendor payment reports to identify 1099 recipients
- Request updated W-9 forms from vendors
- Verify contractor insurance certificates for renewals
- Review security deposit accounting and trust account reconciliation
- Complete annual property inspections
- Update staff training logs
December tasks:
- Finalize vendor payments and 1099 preparation
- Complete annual compliance audit using comprehensive checklists
- Verify all licenses renewed for upcoming year
- Review and update property management agreements
- Submit any required annual reports to state/local agencies
- Plan compliance calendar for 2027
Trust account management requires year-round attention, but December reconciliation ensures you start the new year with clean records.
How Can Technology Simplify Compliance Management?
Manual compliance tracking through spreadsheets and paper calendars doesn’t scale. Property management software transforms compliance from reactive scrambling to proactive planning.
- Automated reminders alert you 30, 14, and 7 days before deadlines. No more missed inspections or late filings because someone forgot to check the calendar.
- Centralized document storage keeps insurance certificates, inspection reports, contractor licenses, Fair Housing policies, and compliance documents organized and accessible. When an inspector asks for your OSHA training records or a tenant requests accommodation documentation, you retrieve it instantly instead of digging through filing cabinets.
- Task assignment and tracking ensures accountability. Assign compliance tasks to specific team members with due dates and completion verification. Management sees exactly what’s completed and what’s overdue.
- Integration with accounting automatically tracks vendor payments throughout the year, making 1099 preparation a simple report instead of a month-long project. W-9 collection becomes part of vendor onboarding, not a January panic.
- Audit trails document every action; who completed inspections, when policies were updated, and which staff completed training. This documentation proves compliance if you face legal challenges or regulatory audits.
Property management platforms that handle operations, financials, and compliance in one system eliminate the gaps where requirements fall through when using multiple disconnected tools.
What Common Compliance Mistakes Should You Avoid?
Even experienced property managers make these errors:
- Mixing compliance deadlines across properties: Managing multiple properties means multiplying compliance obligations. A centralized calendar tracking requirements by property type and location prevents missed deadlines.
- Ignoring state and local variations: Federal rules set baselines, but states and cities often impose stricter requirements. Security deposit return periods range from 14 to 60 days depending on location. Some cities require rental registration; others don’t. Know your specific obligations.
- Treating Fair Housing as a one-time training: Fair Housing violations remain the most common compliance failure. Quarterly training, updated screening procedures, and regular policy reviews keep you compliant. Understanding key performance indicators helps track compliance metrics like consistent screening application rates.
- Failing to document everything: When facing discrimination claims or safety lawsuits, documentation determines outcomes. Keep signed training attendance sheets, inspection reports with photos, accommodation request decisions, and all communications with tenants and vendors.
- Neglecting vendor compliance: Your contractor’s violations become your liability. Require certificates of insurance, verify licenses, ensure proper W-9s on file, and for renovations in pre-1978 buildings, confirm EPA lead-safe certification.
- Delaying safety inspections: “We’ll get to it next month” becomes “We’ll deal with it after the accident.” Maintain strict schedules for smoke detectors, fire extinguishers, emergency lighting, and HVAC systems. OSHA compliance protects tenants, staff, and your business.
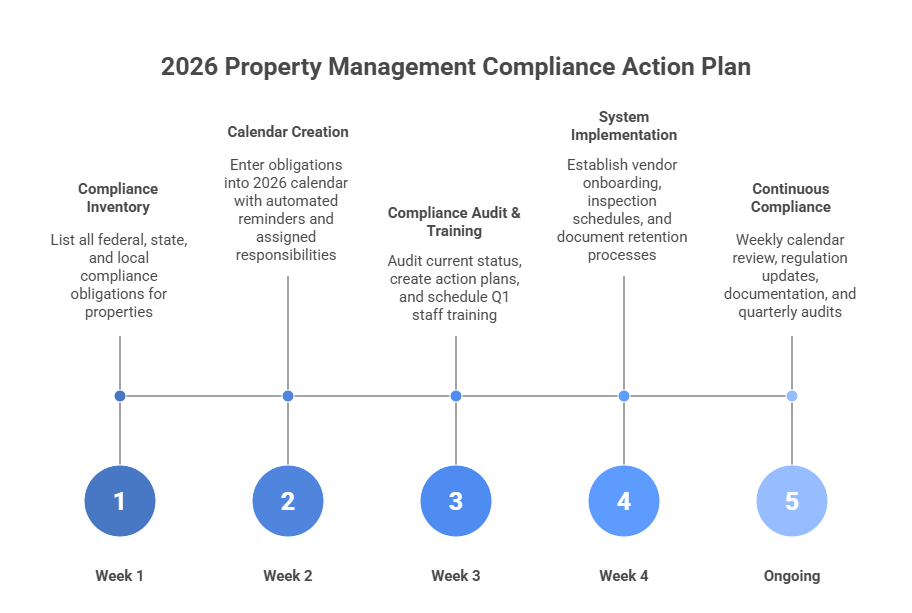
Property management compliance seems overwhelming because obligations come from agencies with different deadlines. But breaking requirements into monthly tasks makes compliance manageable.
The property managers who succeed treat compliance as an operational priority, not an administrative burden. They build systems, leverage technology, train staff, and document thoroughly.
Your 2026 compliance calendar is your roadmap to avoiding penalties, maintaining licenses, protecting your reputation, and providing safe, legal housing to your tenants.
Contact Propertese today to simplify your property management compliance and automate your regulatory tracking.
Table of Contents
Stay Updated
Subscribe to get the latest news, industry trends, blog posts, and updates...