California property management operates under some of the nation’s strictest regulations. The landscape has shifted dramatically with AB 1482’s rent control provisions, AB 12’s security deposit caps, and dozens of local ordinances layering additional requirements on top of state law.
Property managers who fail to navigate this environment face serious consequences. Operating without proper licensing can result in criminal misdemeanor charges and fines up to $20,000 per violation. Fair housing violations carry civil penalties starting at $25,000 for a first offense and climbing to $100,000 for repeat violations. Trust account mishandling, which affected 57% of audited property managers according to California Department of Real Estate data, can lead to license suspension or revocation.
This guide covers the licensing, compliance, lease requirements, financial management, and local variations California property managers must understand to operate legally in 2026.
What License Do You Need for Property Management in California?
The California Department of Real Estate (DRE) requires a real estate license for nearly all property management activities performed for compensation, including listing properties, negotiating leases, collecting rents, and managing rental properties on behalf of owners.
Salesperson vs. Broker License:
A salesperson license allows you to perform property management tasks under broker supervision but prohibits independent operation, signing management agreements in your own name, or holding client funds in trust accounts.
A broker license is required to operate independently, sign management agreements, hold client funds, and serve as the responsible licensee for a property management company.
Educational Requirements:
Salesperson candidates complete 135 hours covering Real Estate Principles (45 hours), Real Estate Practice with mandatory implicit bias and fair housing training (45 hours), and one elective (45 hours).
Broker candidates need two years as a licensed salesperson (or equivalent) within the past five years, plus eight college-level courses including Practice, Legal Aspects, Finance, Appraisal, and Economics or Accounting.
Critical Business Structure Note:
The California DRE does not license LLCs. Only sole proprietorships or corporations can hold broker licenses. If you want LLC benefits, you must form a corporation instead.
For commercial property management operations spanning multiple properties, understanding these licensing distinctions becomes essential for structuring your business correctly.
Common Exemptions:
On-site resident managers (for their property only), employees performing purely clerical functions, property owners managing their own properties, and HOA managers (unless handling leasing) may qualify for exemptions.
How Do Trust Accounts Work in California?
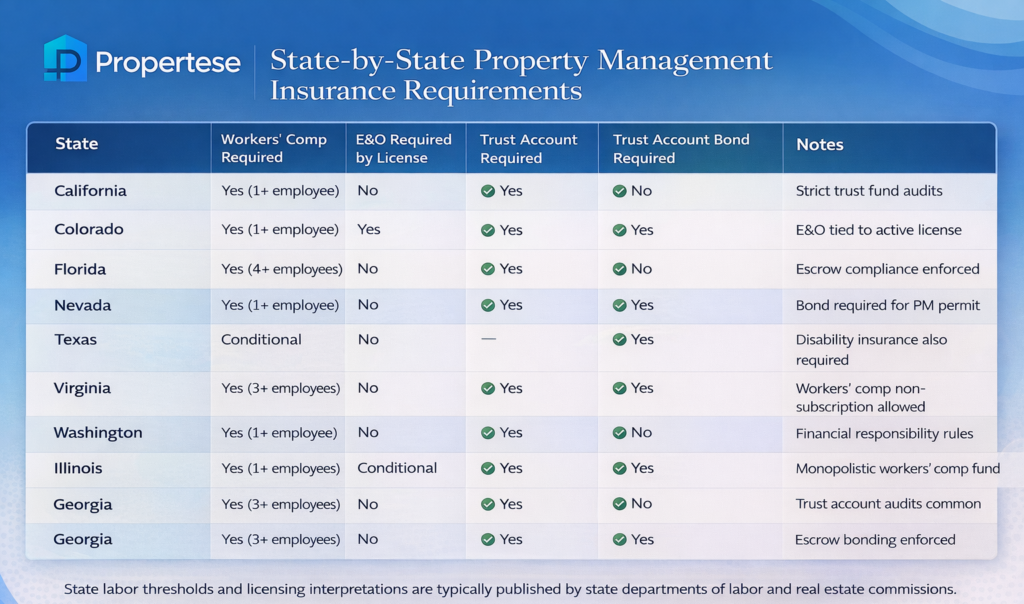
Trust account compliance represents the most common DRE violation area. Property managers must maintain separate trust accounts, follow strict deposit timing, and perform monthly reconciliations.
Setup Requirements:
Open your trust account at a California bank titled “[Broker Name], as Trustee” or “Trust Account.” Keep it completely separate from personal and business accounts. Brokers may deposit a maximum of $200 personal funds for bank fees only.
Deposit Timing:
Deposit all trust funds within three business days of receipt. If acting as an escrow holder, deposit by the next business day.
Record Keeping:
Maintain a columnar record of all trust funds, a record of funds not deposited, separate records for each beneficiary/transaction, and separate records for each property managed using DRE standard forms.
Monthly Reconciliation:
Perform three-way reconciliation monthly, comparing the bank statement, the columnar record, and the sum of all beneficiary ledgers. According to the California Department of Real Estate, nearly one-third of audited property managers show trust account shortages stemming from failure to reconcile monthly or commingling funds.
Effective portfolio management requires robust trust accounting systems tracking funds across multiple properties while maintaining perfect segregation.
What Are California’s Rent Control Requirements Under AB 1482?
AB 1482, the Tenant Protection Act of 2019, established statewide rent control and just cause eviction requirements.
Rent Increase Limits:
Maximum increase is 5% plus local Consumer Price Index (CPI) or 10%, whichever is lower, over 12 months. Maximum two increases per 12-month period. If local CPI is 3.8%, the maximum allowable increase is 8.8%. If CPI is 6%, the maximum remains 10%.
Covered Properties:
Buildings 15 years or older fall under AB 1482. Single-family homes and condos are covered if owned by corporations/REITs or if the landlord failed to provide an exemption notice.
Exempt Properties:
New construction under 15 years old, owner-occupied duplexes, affordable housing with deed restrictions, and properties under more restrictive local rent control.
Just Cause Eviction:
After 12 months of tenancy, landlords can only evict for at-fault causes (non-payment, breach, nuisance, criminal activity) or no-fault causes (owner move-in, withdrawal from market, government order, major renovation, condo conversion).
No-fault evictions require one month’s rent relocation assistance. SB 567 amendments mandate owners actually move in within 90 days, maintain primary residence for 12 months, and offer the unit back to tenants if these conditions aren’t met.
How Have Security Deposit Rules Changed?
AB 12, effective July 1, 2024, dramatically reduced security deposit limits.
General Rule:
Maximum security deposit is one month’s rent for furnished and unfurnished units. This cap includes pet deposits and “last month’s rent”; everything counts toward the one-month limit.
Small Landlord Exception:
Natural persons or LLCs (all members natural persons) or family trusts owning two or fewer properties totaling four or fewer units may collect up to two months’ rent.
Move-In/Move-Out Documentation:
AB 2801, effective January 1, 2025, requires photo and video documentation at move-in and move-out. Retain this documentation as evidence for deposit deductions.
Return Requirements:
Return deposits within 21 days with itemized statements. Include receipts for repairs over $126. Late return forfeits your right to retain any deposit. Bad faith retention can result in statutory damages up to twice the deposit.
For residential property management companies handling hundreds of turnovers annually, these documentation requirements demand systematic processes.
What Fair Housing Laws Apply in California?
California’s fair housing protections extend beyond federal requirements.
Protected Classes:
Federal law protects race, color, national origin, religion, sex, familial status, and disability. California adds ancestry, marital status, age, sexual orientation, gender identity, medical condition, genetic information, source of income, military/veteran status, citizenship/immigration status, and primary language.
Source of Income Protection:
Property managers must accept Section 8 Housing Choice Vouchers and rental assistance. According to the California Department of Justice, source of income discrimination represents a major enforcement priority.
Criminal History Screening:
Cannot automatically deny based on criminal records. Denials must be directly related to tenant fitness and safety. Consider nature/severity, time elapsed, and rehabilitation through individualized assessments.
Reasonable Accommodations:
Assistance and service animals aren’t pets. No pet deposits/fees allowed for assistance animals. Cannot deny based on breed, size, or weight. Must allow modifications at tenant expense.
Penalties:
First violation: $25,000. Second within five years: $50,000. Third+ within seven years: $100,000. Private lawsuits can result in unlimited damages including emotional distress, punitive damages, and attorney fees.
What Disclosures Must California Property Managers Provide?
Universal Disclosures:
Megan’s Law sex offender database notice, bed bug information, landlord contact information, shared utility meter arrangements, and smoking policy.
Conditional Disclosures:
Lead-based paint (pre-1978 buildings) with EPA pamphlet and disclosure form, toxic mold information if known, methamphetamine contamination with remediation order copy ($5,000 penalty for failure to disclose), death in unit within three years, ordnance locations within one mile of military base, pest control pesticide information, water billing arrangements if separate.
Late Fee Limitations:
Late fees must be reasonable. Courts generally accept 4-5% of monthly rent or $50-$100 flat fees. Daily fees acceptable if reasonable ($5-$10/day). Include in lease and apply consistently.
Understanding property and unit management requirements ensures no disclosure falls through the cracks.
How Do California Eviction Procedures Work?
California eviction procedures are technical. Mistakes invalidate the entire process.
Notice Types:
Three-day notice to pay rent or quit for non-payment (exact amount due, where/when/how to pay). Three-day notice to cure or quit for curable violations (specify what to fix). Three-day unconditional quit for serious violations (no cure opportunity). 30-day notice for month-to-month under one year. 60-day notice for month-to-month one year or longer. 90-day notice for subsidized/Section 8 housing.
Court Process:
File unlawful detainer complaint ($240-$450 filing fee). Serve summons and complaint. Tenants have 10 business days to respond (extended from five days under AB 2347). Trial if contested or default judgment if uncontested. Request writ of possession. Sheriff posts five-day notice then performs lockout.
Timeline:
Uncontested: 30-45 days minimum. Contested: 60-90+ days. Complex cases: 4-6 months.
Relocation Assistance:
State law (AB 1482): one month’s rent. Los Angeles: $8,900-$26,700+. San Francisco: $6,756-$11,709+. Oakland and San Jose have similar requirements. Always check local ordinances.
How Do Major California Cities Differ?
Los Angeles:
Rent Stabilization Ordinance covers pre-October 1978 buildings with 2+ units. Increases limited to 3-4% annually. Must register with LAHD. Business license: $45-$800+.
San Francisco:
Strictest rent control for pre-June 1979 buildings. Rent Board sets annual increases (2-3%). Security deposits earn 5.0% annual interest. All units must register. Business license: $91-$500+.
San Diego:
Follows AB 1482 without additional local rent control. Business license: $34-$125. Monitoring new regulations on algorithmic rent setting.
Oakland:
Rent Adjustment Ordinance covers pre-1983 buildings with 2+ units. CPI-based increases (2-3%). Security deposit interest required. Must register. Business license: $125+.
San Jose:
Apartment Rent Ordinance covers pre-September 1979 buildings with 3+ units. 5% annual or 8% with capital improvements. Must register. Business license: $50+.
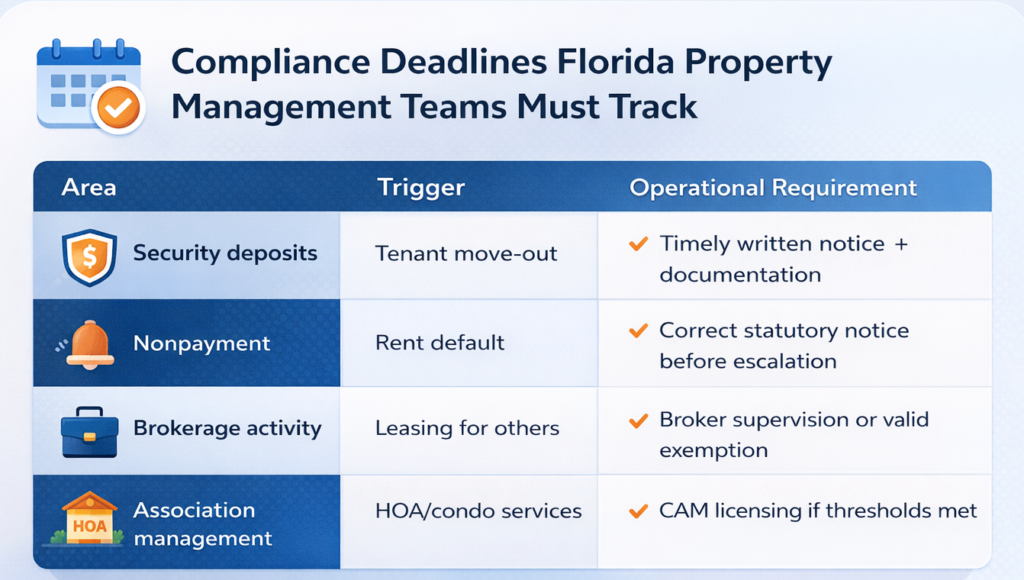
A comprehensive property management compliance calendar helps track different deadlines across cities.
What Professional Certifications Should You Consider?
Certifications are optional beyond the mandatory DRE license, but demonstrate expertise.
Institute of Real Estate Management (IREM): Certified Property Manager (CPM®) requires 36 months of experience, 25+ units managed, approximately $6,200 in fees, $495 annual dues.
National Association of Residential Property Managers (NARPM): Residential Management Professional (RMP®) requires two years of experience, 100+ units, broker license, $270 annual dues. Master Property Manager (MPM®) requires RMP first and 500+ units.
National Apartment Association (NAA): Certified Apartment Manager (CAM) requires 12 months of experience, 40 hours of coursework, and approximately $900 in fees.
What Technology Do California Property Managers Need?
Property Management Software:
Choose platforms designed for California trust accounting with features including trust account compliant accounting, online rent payment, tenant/owner portals, maintenance tracking, lease management, automated late fees, 1099 generation, and bank reconciliation.
According to Property Management Insider, property managers using specialized software experience 40% fewer compliance violations compared to generic accounting software.
Document Management:
Secure cloud storage for leases, applications, and inspection photos with audit trails, version control, electronic signatures, and mobile access.
What Resources Help California Property Managers Stay Compliant?
Government Resources: California Department of Real Estate (dre.ca.gov), California Department of Justice (oag.ca.gov/fair-housing), and local rent boards offer licensing information, trust account guidance, and ordinance details.
Industry Associations: California Apartment Association (caanet.org), IREM, NARPM, and NAA provide legislative updates, legal advice, forms, and training.
Professional Support: Retain a real estate attorney familiar with California landlord-tenant law and an accountant who understands trust accounting requirements.
Understanding California property management requirements and staying current with ongoing changes represents a challenging aspect of the business. Property managers who invest in proper licensing, robust compliance systems, professional development, and expert advisors position themselves for long-term success.
Contact Propertese today to centralize your trust accounting, automate compliance tracking, and manage documentation for every California jurisdiction you operate in.